Facilities
Our Facilitites
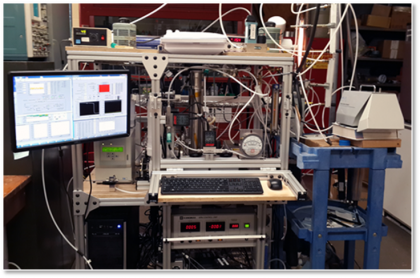
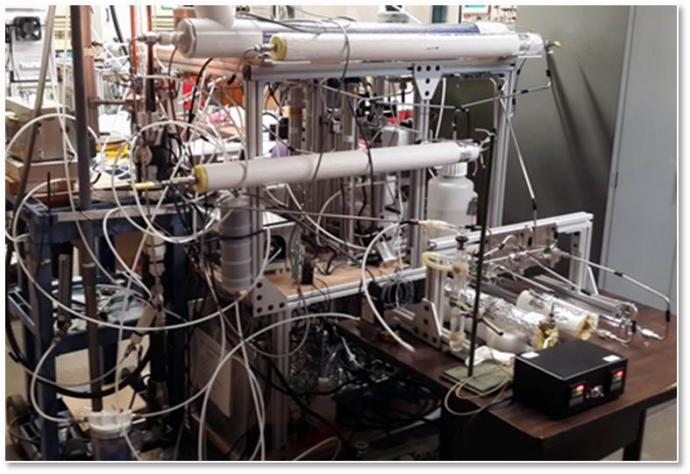
Aerosol system
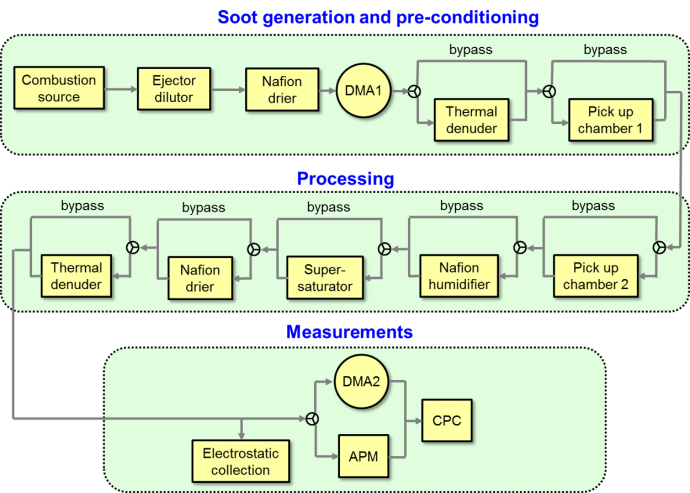
The system is used to generate airborne particles of different compositions and morphologies, subject the particles to simulated atmospheric processing, and measure the response in the particle properties. It consists of a constant output atomizer, an inverted diffusion burner, two Differential Mobility Analyzers, an Aerosol Particle Mass analyzer, a Condensational Particle Counter, saturator and condenser chambers, thermal denuders, an electrostatic particle collector. This system has been used to complete a collaborative research project with Prof. Chong Qiu (University of New Haven) to measure thermochemical properties of atmospherically relevant monoethanolaminium salts. Currently, this system is the working horse in the NSF-supported NJIT-led collaborative project to investigate the morphology and optical properties of soot nanoparticle aggregates.
|
|
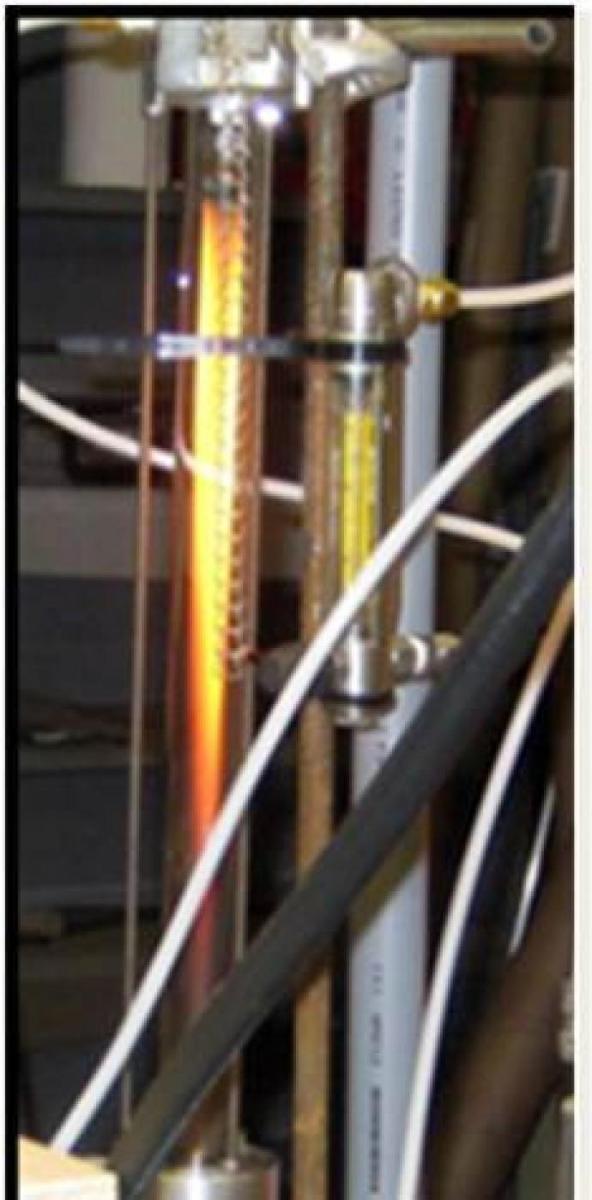
Inverted diffusion burner |
|
An Integrating nephelometer and a Cavity Attenuated Phase Shift spectrometer (CAPS)
The nephelometer and CAPS are used to measure light scattering and extinction coefficients by aerosols particles. Light absorption can be then determined as the difference between extinction and scattering. Associated cross sections (specific and per particle) are calculated by using independently measured particle mass and number density.

An Ion Drift - Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer
This highly sensitive instrument can detect organic and inorganic trace gas molecules down to a part-per-trillion concentration level. The instrument is used in laboratory kinetic and mechanistic studies of gas-phase and surface reactions and in field measurements of air pollutants. This instrument is the working horse of the NSF CAREER project to investigate the molecular mechanisms of the atmospheric mercury oxidation.


Glass and stainless manifolds for preparation of gas mixtures

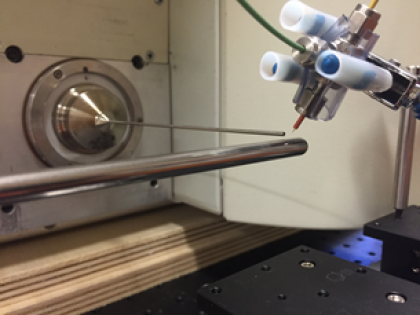
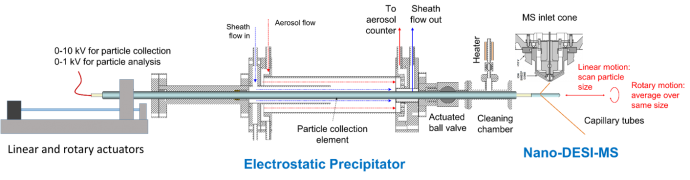
Chemical analysis of aerosol nanoparticles
This instrument comprises an Electrostatic Particle Collector (EPC) integrated with Desorption Electrospray Ionization (DESI) and a Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (TQMS). The mass spectrometer was donated by the Lundbeck Research, USA. The EPC has been developed with partial support from the NJIT Faculty Seed Grant (2014).
The adsorption-ultrasound system
The current experimental setup can be used to study porous materials exposed to water vapor. The saturation ratio of water is controlled using a series of solutions of salts with different deliquescence points. Overall, the system comprises a humidity-controlled chamber (left pane) into which a porous sample with two ultrasonic transducers held in place by a sample holder (righ pane) is loaded. One transducer serves as the ultrasound wave source and another serves as the reciver. The source transducer is excited using a short, 50-70 ns, pulse generated by the pulser, producing a mechanical 5 MHz waveform. The electrical pulse generated by the waveform arriving at the receiving transducer is amplified by the receiver and recorded with a digital oscilloscope (middle pane).